44g. The Panama Canal
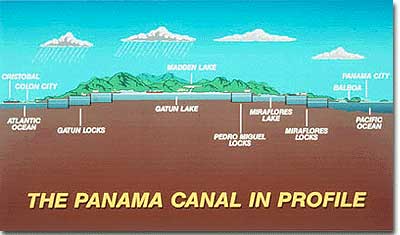
A view of the Panama Canal in profile, showing the placement of the locks.
A canal was inevitable. A trip by boat from New York to San Francisco forced a luckless crew to sail around the tip of South America — a journey amounting to some 12,000 miles. The new empire might require a fast move from the Atlantic to the Pacific by a naval squadron. Teddy Roosevelt decided that the time for action was at hand. The canal would be his legacy, and he would stop at nothing to get it.
First Obstacles
There were many obstacles to such a project. The first was Great Britain. Fearing that either side would build an isthmathian canal and use it for national advantage, the United States and Great Britain agreed in the 1850 Clayton-Bulwer Treaty that neither side would build such a canal. A half century later, the now dominant United States wanted to nullify this deal. Great Britain, nervous about its South African Boer War and an increasingly cloudy Europe, sought to make a friend in the United States. The Hay-Pauncefote Treaty permitted the United States to build and fortify a Central American canal, so long as the Americans promised to charge the same fares to all nations. One roadblock was clear.
Selecting Panama
The next question was where to build. Ferdinand de Lessups, the same engineer who designed the Suez Canal, had organized a French attempt in Panama in the 1870s. Disease and financial problems left a partially built canal behind. While it made sense that the United States should buy the rights to complete the effort, Panama posed other problems. Despite being the most narrow nation in the region, Panama was very mountainous, and a complex series of locks was necessary to move ships across the isthmus. Nicaragua was another possibility. The canal would be situated closer to the United States. The terrain was flatter, and despite Nicaragua's width, there were numerous lakes that could be connected. Volcanic activity in Nicaragua prompted the United States to try to buy the territory in Panama.
But Panama was not an independent state. To obtain the rights to the territory, the United States had to negotiate with Colombia. The 1903 Hay-Herran Treaty permitted the United States to lease a six-mile wide strip of land at an annual fee. The treaty moved through the United States Senate, but the Colombian Senate held out for more money. Roosevelt was furious. Determined to build his canal, Roosevelt sent a U.S. gunboat to the shores of Colombia. At the same time, a group of "revolutionaries" declared independence in Panama. The Colombians were powerless to stop the uprising. The United States became the first nation in the world to recognize the new government of Panama. Within weeks, the Hay–Bunau-Varilla Treaty awarded a 10-mile strip of land to the United States, and the last hurdle was cleared.
Constructing the Canal
Or so it seemed. Construction on the canal was extremely difficult. The world had never known such a feat of engineering. Beginning in 1907, American civilians blasted through tons of mountain stone. Thanks to the work of Walter Reed and William Gorgas, the threats of yellow fever and malaria were greatly diminished. When Theodore Roosevelt visited the blast area, he became the first sitting American President to travel outside the country. Finally, the deed was done. In 1914, at the cost of $345 million, the Panama Canal was open for business.






